The use of VPNs has increased dramatically in recent years, with over 31% of internet users (that’s over 1.2 billion people) reporting that they use a VPN in 2025. And that number is almost certain to increase in the coming years as online security threats increase and internet users search for ways to protect their identities and information online.
But what exactly is a VPN, and what does it do to your internet speed?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a service that protects the security and anonymity of your internet connection. It does this by disguising your IP address and creating an encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic to flow through.
In essence, a VPN makes it impossible for other websites or entities on the internet to know exactly where your computer is located. It also protects your internet activity and data from being viewed (or stolen) by malicious actors.
Using a VPN comes with a slew of benefits for anyone, from journalists working under oppressive governments to people who just want to access their favorite streaming service from a different country than the one they’re physically located in.
However, speed is not one of the benefits of using a VPN: on the contrary, using a VPN generally slows down your internet speed.
Summary: Do VPNs Make Your Internet Faster?
VPN’s added layer of encryption (plus the ability to connect to servers that are geographically far from your physical location) can slow down your internet speed.
However, there are a few instances in which using a VPN can actually increase your speed and make your internet faster. This can happen when the slowdown is caused by your internet service provider throttling your internet traffic or routing it through a slow server.
Why Does Using a VPN Slow Down Your Internet?
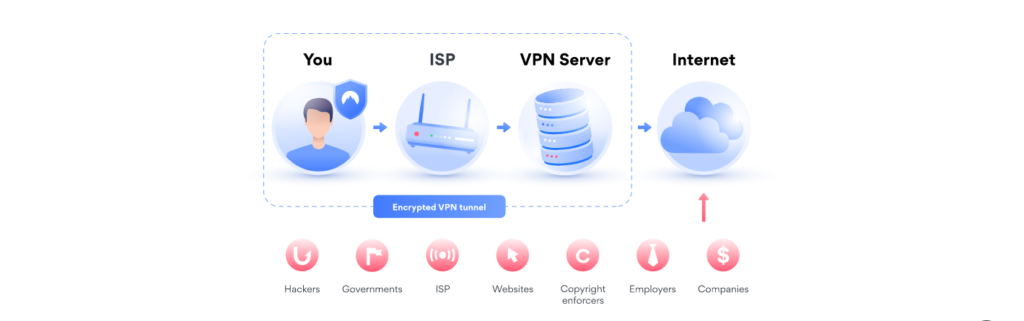
To put it simply, it’s because using a VPN adds extra steps that have to be accomplished when you try to do anything on the internet. First, the VPN encrypts your connection. Then, it routes your traffic through a VPN server.
This second step can be slowed down even further if you are physically very far from the server you’re trying to connect through. Most VPN providers allow you to choose a country where you want your internet access to be routed through.
So, if you live in Australia and you want to connect to a VPN server to watch UK TV, it’s going to slow down the connection more because of the geographical distance between the two.
Even though all of this happens in a matter of milliseconds, it does still technically make the process slower.
There are a few tips and tricks you can try to minimize the slowdown. First, you should make sure that your ISP (internet service provider) isn’t the problem causing the slowdown. If you already have a sluggish internet connection, then using a VPN certainly isn’t going to make things faster.
You can also choose to connect through VPN servers in nearby countries (or in your own country, if the point is simply to encrypt your connection), thus minimizing the geographical distance problem.
Finally, you should do your research. There are tons of good VPN providers on the market today, and not all are created equal.
Some are known for having faster speeds and less latency than others, and it’s worth investing in a high-quality VPN that will function smoothly and keep your data secure.
On the topic of security, there is a bit of a trade-off: better security encryption protocols often mean slightly slower speeds.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is the standard encryption protocol used by most VPNs, and it comes in various different grades. For example, one of the most secure is AES 265-bit encryption, but there are lower levels as well, such as AES 128-bit.
It’s generally advisable to look for a VPN with the strongest possible encryption because it means your data and traffic will be protected with the highest industry standards.
However, if speed is your top priority, then you may actually want to find a provider that uses a lower grade of AES, as this will likely provide a slight boost in speed.
With that said, it’s also worth remembering that we’re talking about very, very small reductions in speed: particularly if you’re using a good VPN, you very likely won’t notice any slowdown at all.
Realistically speaking, the only people who would likely notice and be bothered by the difference in speed caused by using a VPN are those who want to do international financial and other trade transactions in which even milliseconds can make a huge difference.
When Does Using a VPN Make Your Internet Faster?

Although using a VPN slows down your internet speed in most cases, there are a few situations in which it can actually help make your internet faster.
In cases of bandwidth throttling or inefficient ISP (internet service provider) routing, using a VPN can help you circumvent these issues and make your internet faster as a result.
Let’s take a look at these situations and how using a VPN can be beneficial for getting around them.
Bandwidth Throttling
Occasionally, ISPs will intentionally slow down their customers’ internet traffic. This is called bandwidth throttling or just throttling. It’s usually targeted at specific types of traffic, such as streaming services.
This is often done in an attempt to make sure that resources are distributed evenly amongst all of an ISP’s customers and to keep things running smoothly for everyone.
As such, it’s not always a bad thing, but it can definitely be annoying when you’re trying to live stream the big game and every play is interrupted by lagging and freezing.
If your ISP is throttling your internet, a VPN can solve this problem for you by getting around the artificial slowdown. How?
Remember that a VPN encrypts your internet traffic so that no one – including your ISP – can see which websites you’re trying to access.
Since bandwidth throttling is almost always targeted at specific types of websites – like streaming services – using a VPN makes it impossible for your ISP to know what types of website you’re accessing, thus making it impossible for them to throttle your communication speed.
Inefficient ISP Routing
Another problem that using a VPN can help alleviate is inefficient ISP routing. To put it simply, your ISP doesn’t always route your internet traffic through the fastest server.
This is because ISPs attempt to evenly distribute resources, so it isn’t technically a bad thing. But still, it can be annoying on those days when your internet connection seems hopelessly, inexplicably slow.
A VPN can also help with inefficient ISP routing because it sends your internet traffic through its own servers (or the servers that you’ve chosen).
Particularly if you let your VPN choose a server to route your traffic through rather than manually setting it, the VPN will choose the fastest available server, thus getting around any potential slowdowns caused by your ISP.
Summary – Do VPNs Make Your Internet Faster?
Overall, using a VPN has tons of benefits, but speed is generally not one of them.
A VPN makes it possible for you to protect your data and your identity when you’re connected to the internet, and it increases your flexibility when it comes to circumventing geo-blocked content and circumventing local internet restrictions.
However, the added layer of encryption (plus the ability to connect to servers that are geographically far from your location) can slow down your internet speed.
This usually isn’t a significant slowdown, however, so it likely won’t be a problem for most people using a reliable, high-quality VPN like ExpressVPN, NordVPN, PIA, CyberGhost, AtlasVPN, or Surfshark.
Paradoxically, there are a few instances in which using a VPN can actually increase your internet speed. This can occur when the slowdown is caused by your internet service provider throttling your internet traffic or routing it through a slow server – both instances in which a VPN would circumvent those problems.
But other than these specific instances, you can expect to see either no noticeable change or only a minor decrease in speed when using a VPN.
References:
https://nordvpn.com/what-is-a-vpn/
