Online safety should be one of your top concerns whenever your computer, phone, or other device is connected to the internet. However, with an ever-increasing number and range of scams, threats and other malware attacks, it can be hard to know what a VPN protects you from.
A VPN, or virtual private network, is an incredible tool with a wide range of applications. Research has shown that at least 1.2 billion people around the world use a VPN, and its popularity is growing rapidly.
Although it can’t solve all of your security problems (for a comprehensive approach to security, you’ll need a strong antivirus software solution), a VPN can protect your internet traffic and identity from a wide range of threats.
Read on to find out what kind of attacks a VPN can prevent, how it works, and what its limitations are.
Key Points: How & What Does a VPN Protect You From?
- Although a VPN isn’t a magic shield against all potential dangers, using a VPN can hide and protect you from an impressive range of online threats.
- These include many types of hacking, man-in-the-middle and DDoS attacks, fake WiFi hotspots, and much more.
- Even if you are protecting your device and your privacy with a VPN, it’s important to remain vigilant and careful when you’re browsing online – a VPN can’t protect you from your own error.
What Does a VPN Prevent?
Although a VPN can’t protect you from every potential threat, it can prevent an impressively wide range of malicious attacks – particularly those that use WiFi or other internet connection-related techniques to get ahold of your private information.
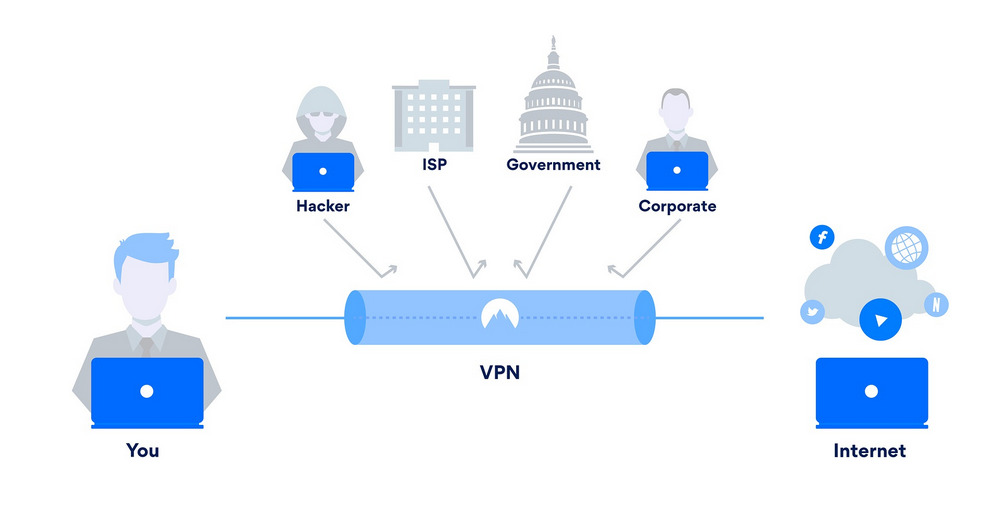
So, what exactly can a VPN help protect you from?
Some Types of Hacking
First of all, it’s important to note that a VPN can’t protect you from every kind of hacking. With that said, a VPN can protect you from a pretty impressive range of hacking threats.
First, by disguising your IP address, a VPN makes it effectively impossible for malicious actors to track your computer’s location.
One of the most common, tried-and-true remote hacking methods involves gaining access to your computer’s system through its IP address.
Considering that pretty much every website you visit tracks your device’s IP address (yes, that includes phones and tablets as well), if any of those websites have been infiltrated by a hacker, it’s only too easy for them to obtain your IP address and use it to get into your computer system.
Thus, by masking your device’s real IP address, a VPN can keep your device protected from this all-too-common type of hacking.
Man-In-The-Middle Attacks
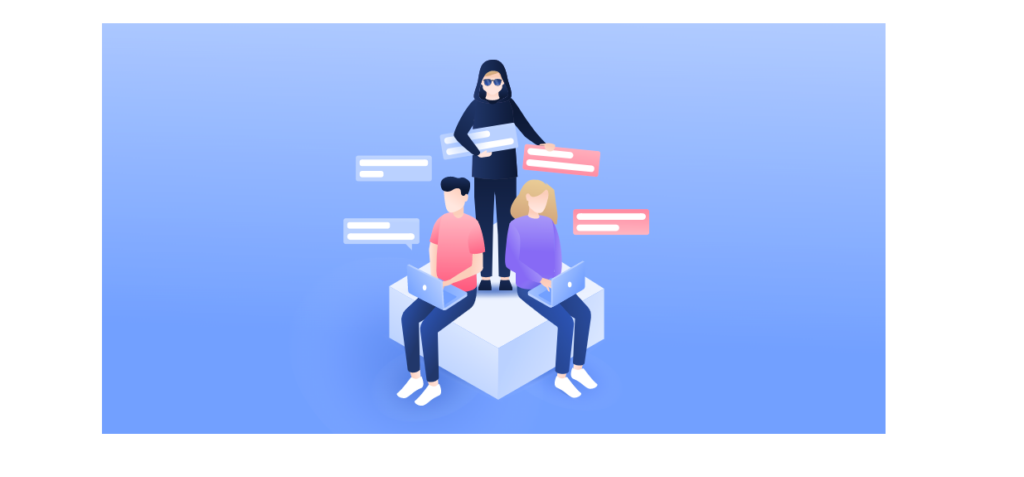

A man-in-the-middle attack is exactly what it sounds like: a hacker intercepts your internet traffic “in the middle”, when your device is communicating with a website or web server.
Man-in-the-middle attacks are particularly dangerous because they can easily be used to steal your private information, including passwords, files, online banking and credit card information, and much more.
Although man-in-the-middle attacks aren’t impossible when using a private WiFi connection (such as the WiFi in your home), they are particularly likely when you’re using an open, public WiFi connection, such as those found in cafés, restaurants, libraries, universities, or other public spaces.
This is because it’s advantageous for hackers to target public WiFi connections that large numbers of people connect to every day. Additionally, most WiFi – both public and private – use an encryption standard called WPA2, which is, unfortunately, one of the lowest security standards.
So, how does a VPN protect you from man-in-the-middle attacks? By creating an encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic to travel through, it makes it very difficult for your internet traffic to be intercepted and stolen.
As such, it’s always advisable to run your internet traffic through a VPN whenever you’re connecting your device to a public WiFi network.
DDoS Attacks

DDoS, or Distributed Denial of Service attacks, are another form of hacking that a VPN can successfully prevent.
In a DDoS attack, hackers attempt to overwhelm your system by flooding it with requests and uninvited traffic. This causes the system to crash, which can either force you offline or make it impossible for you to access a particular website.
DDoS attacks are unfortunately becoming more common, as they aren’t particularly difficult for even entry-level hackers to execute. However, using a VPN can protect you from DDoS attacks in the same way it protects you from other forms of hacking: by disguising your IP address.
In order for a DDoS attack to target your device, it has to know your real IP address first. As long as you consistently use a VPN when connecting to the internet, malicious actors will have no way of gaining access to your real IP address.
Fake WiFi Hotspots

Another risk that your VPN can help mitigate is fake WiFi hotspots. Also known as an “evil twin” hotspot, a fake WiFi hotspot is created by a hacker to carefully mimic the exact look of a legitimate WiFi hotspot, right down to identifying details like the SSID (service set identifier or name of the WiFi network).
For example, let’s say you’re sitting in a café called Main Street Café. You ask the barista which WiFi network to connect to, and she tells you it’s a network called mainstreetcafe123. If a hacker has set up a fake WiFi hotspot to target traffic coming from this location, the fake hotspot can also be called mainstreetcafe123.
As soon as you connect your device, the hacker will have easy access to all of your internet traffic. That means they can steal your passwords, account names, and any files you download or upload while you’re connected to their network.
So how can a VPN protect you from this? After all, didn’t you unwittingly choose to connect to the fake network?
The key to protection in this situation is the fact that a VPN encrypts all of your internet traffic and all communication between your device and any web servers. Thus, even if you do accidentally connect to a fake WiFi network, hackers still won’t be able to capture or see anything that you’re doing online.
How Does a VPN Protect You From Hacking?
A VPN works on two basic levels:
- by disguising your IP address (the address that identifies and locates your computer), AND
- by creating an encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic to go through.
Some VPN providers offer even further levels of protection, but this is the general idea. Since gaining access to your device’s IP address is one of the most common methods of hacking, disguising it from hackers is a great way to protect yourself.
Further, channeling all of your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel helps keep your information safe even if your system is compromised.
What Else Does a VPN Protect?
The internet is a vast and complex network, and while it provides us with countless benefits, it also exposes us to various risks and threats.
From cybercriminals to advertisers, many third parties can track your online activities, monitor your internet traffic, and collect your personal data, including your browsing histories, search history, and even your browser fingerprint.
Fortunately, there are various security measures you can take to protect yourself and your sensitive information.
For instance, you can use internet security software and antivirus programs to safeguard your devices from malware and computer viruses.
You can also use VPNs to encrypt your internet traffic and hide your IP address, making it difficult for others to monitor your online activities.
Additionally, a kill switch can help you automatically disconnect from the internet if your VPN connection drops, ensuring that your data remains secure and private.
By taking these measures and being vigilant about data breaches and other potential threats, you can enjoy a safer and more secure online experience.
In addition to protection from hackers, a VPN is also an invaluable tool for protecting your privacy when you’re surfing the web.
By encrypting your traffic, a VPN helps keep your searches, downloads, and other activities hidden from prying eyes. There’s a huge market out there for all of our private data, and most websites collect information about who accessed them and what they did.
When you’re using a VPN, your activity on the internet won’t be visible to most websites that track your searches and purchasing behavior to target you for advertising.
This means no more annoying ads that pop up on the side of your web browser the second you search for a product or related keyword.
How Does a VPN Protect Your Privacy?
To summarize, a VPN protects your privacy primarily by disguising your IP address and creating a safe, encrypted passage for your internet traffic to travel through.
If hackers and other malware can’t see what you’re doing online, they can’t steal it. Similarly, if adware and websites that track visitors’ activities can’t see what you’re doing, they can’t target you for advertising.
Privacy is getting harder and harder to preserve when you’re online, but using a VPN is a simple, relatively inexpensive way to protect your online activities from prying eyes.
What Won’t a VPN Protect You From?
When you connect to the internet, your internet service provider (ISP) assigns your device a unique IP address, which is used to identify and track your online activities.
This is true whether you are using a public Wi-Fi network or a home network.
When using public Wi-Fi networks, you are at a greater risk of having your network access compromised, making it easier for third parties to monitor your internet traffic and steal sensitive information, such as your login credentials for streaming services.
To protect yourself, it is important to use a VPN, which can help you hide your IP address and encrypt your internet connection, making it more difficult for anyone to monitor your online activities.
Additionally, you should always keep your operating system and applications up to date to minimize the risk of security vulnerabilities. By taking these precautions and being aware of the potential risks, you can enjoy safer and more secure streaming content while using the internet.
All of this sounds amazing, but let’s not get too carried away: a VPN can’t protect you from every kind of threat, and it’s important to be realistic about what it can and can’t do.
Human Error
Unfortunately, a VPN can’t protect you from yourself. The IBM Cyber Security Index has reported that a whopping 95% of all cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error.
This usually comes in the form of malware that people have unintentionally installed on their own devices or phishing schemes, where people are tricked into giving up their passwords to malicious actors.
In other words, the overwhelming majority of attacks are accidentally enabled by people who don’t realize what they’re doing. Unfortunately, a VPN can’t stop you from doing something that you’ve willingly chosen to do, which is why it’s crucial to stay vigilant and skeptical whenever you’re online.
A good rule of thumb is that if something seems fishy, you should trust your gut and stay away from it.
Untrustworthy VPNs
The other thing that a VPN can’t protect you from is itself. If you’ve chosen an untrustworthy VPN provider, your device’s security will very likely be compromised.
That’s why it’s extremely important to do the research and choose a trustworthy, highly secure VPN provider.
This generally means being willing to pay for quality. There are a ton of free VPNs on the market, but as the old saying goes, there’s really no such thing as a free lunch: these “free” VPNs are making money somehow, and it’s usually by selling their users’ data to third parties.
If you’re looking for a VPN and you’re not sure where to start looking, you can check out my list of the best VPN providers on the market today.
Summary – What a VPN Can and Can’t Protect You From?
There are tons of benefits that you can reap from using a VPN, from majorly increased security and privacy when you’re online to the ability to disguise your location and connect to the internet through foreign servers.
Although VPNs aren’t magical shields that can protect you from everything, there are tons of everyday threats that can be neutralized simply by using a VPN. These include having your private information stolen by DDoS attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and fake WiFi hotspots.
A VPN can also help you avoid being tracked online (with some limitations and exceptions) and makes it easy to bypass ISP restrictions and geo-blocking.
All in all, in a world of ever-increasing security threats, investing in a trusted, high-quality VPN is a fantastic and almost effort-free way to stay protected while you’re online.
References
- https://i.crn.com/sites/default/files/ckfinderimages/userfiles/images/crn/custom/IBMSecurityServices2014.PDF
- https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/social-media/timeline-facebook-s-privacy-issues-its-responses-n859651
- https://www.vanityfair.com/news/2020/01/facebook-settlement-facial-recognition-illinois-privacy
- https://nordvpn.com/blog/man-in-the-middle-attack/
- https://nordvpn.com/blog/what-is-a-ddos-attack/
- https://nordvpn.com/blog/securing-public-wi-fi/
